HMPV Outbreak in China: Check How Does HMPV Spread, Who is Most at Risk?
Learn about the recent HMPV outbreak in China, its symptoms, transmission, and preventive measures. Stay informed about this respiratory virus affecting vulnerable populations.
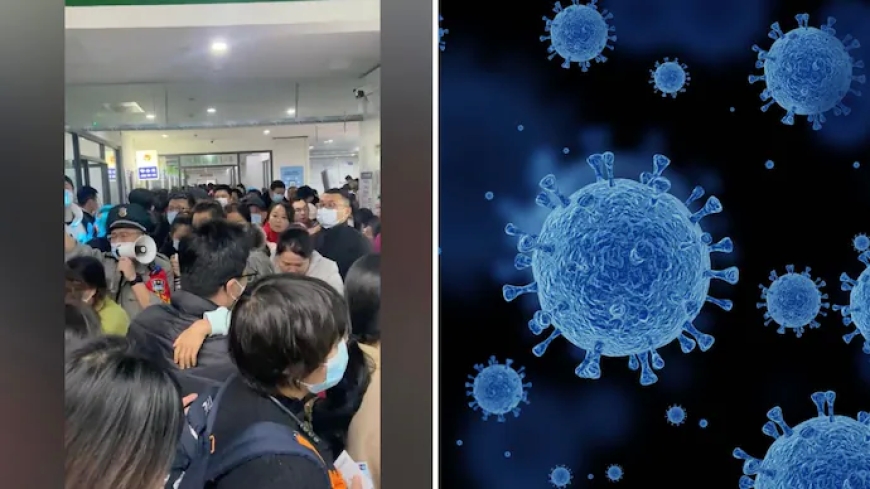

China is currently experiencing a surge in human metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases, raising concerns about another potential health crisis in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Reports and social media posts highlight overcrowded hospitals, with some suggesting the presence of multiple viruses, including HMPV, influenza A, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and COVID-19.
HMPV, a respiratory virus that causes flu-like symptoms, can lead to severe respiratory complications, especially in children and vulnerable populations. Here’s what you need to know about this emerging outbreak.
What is HMPV, and Why is it Making Headlines in China?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that causes upper and lower respiratory infections. It was first identified in 2001 and can infect people of all age groups. However, young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Symptoms of HMPV
The symptoms of HMPV resemble those of influenza and other respiratory infections. Common signs include:
-
Cough
-
Fever
-
Nasal congestion
-
Shortness of breath
In severe cases, HMPV can lead to complications such as bronchitis or pneumonia. The incubation period ranges from three to six days, with the duration of symptoms varying based on the severity of the infection.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads similarly to other respiratory viruses, through:
-
Respiratory droplets from coughing and sneezing
-
Close personal contact, such as shaking hands
-
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes
Who is Most at Risk?
According to the CDC, the groups most vulnerable to HMPV include:
-
Young children
-
Older adults
-
Individuals with weakened immune systems
Prevention Measures for HMPV
Preventive steps are critical to reducing the spread of HMPV. These include:
-
Washing hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
-
Avoiding touching your face with unwashed hands.
-
Maintaining distance from individuals showing signs of illness.
-
Regularly cleaning frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs and toys.
What to Do If You Experience Symptoms
If you or a loved one experience symptoms of HMPV, follow these steps to prevent further spread:
-
Cover your mouth and nose: Use a tissue when sneezing or coughing.
-
Practice good hand hygiene: Wash hands frequently for at least 20 seconds.
-
Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share utensils, cups, or personal items.
-
Stay home: Rest and avoid contact with others to reduce the risk of transmission.
Is There a Treatment or Vaccine for HMPV?
Currently, no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine exists for HMPV. Medical care focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Severe cases may require hospitalization.
How Does HMPV Compare to COVID-19?
HMPV and COVID-19 share several similarities, including respiratory symptoms such as coughing, fever, nasal congestion, sore throat, and shortness of breath. Both viruses spread through respiratory droplets and can lead to severe complications requiring hospitalization.
However, HMPV typically peaks during winter and spring, whereas COVID-19 has demonstrated year-round transmission due to its evolving variants. Additionally, studies suggest that respiratory infections like HMPV have surged in some regions after COVID-19 restrictions were lifted. Experts believe reduced exposure to viruses during lockdowns weakened immunity, leading to the current spike in cases.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0